ㅁ 데이터 불러오기
0. 공통
import pandas as pd
import os
try:
os.chdir("C:/Users/gykwa_u2aecfe/OneDrive/바탕 화면/sample_data") # 사용하고자 하는 txt 문서가 있는 파일 이름까지 입력
print("Directory changed")
except OSError:
print("Cannot change the current working directory")
1. txt
pd.read_table("people.txt", sep= ' ', header = 0, encoding="UTF-8") #txt 이름, 셀 구분 기준, 행, 인코딩 순서
2. xlsx
pd.read_excel('Financial Sample.xlsx')3. csv
pd.read_csv('train.csv')
# 데이터 출처 : https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/heptapod/titanic>>>

ㅁ 데이터 조작
1. 행에 이름 부여하기
titanic_raw = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
titanic_raw.index = [x for x in range(1,892)]
titanic_raw2. loc과 iloc
loc : location의 약자로, label 형태로 접근
iloc : integer location , 인덱스 값으로 접근
titanic_raw.loc[[2,3]]
titanic_raw.iloc[1:3]
titanic_raw.iloc[3,0:2] #'3'행의 0,1 에 해당되는 값 printㅁ데이터 병합
1. merge
pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key') 형태로 사용
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'customerID' : range(1,4), 'commodity' : ('apple '*2 +'banana '*2).split()})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'customerID' : [2,5], 'Gender' : ['male', 'female']})
df3 = pd.merge(df1, df2, on = 'customerID')>>>

<merge의 종류>
1. Inner : 교집합
2. Outer : 합집합, 없는 데이터에 대해선 NaN으로 표시
3. Left Outer : 첫번째 df를 기준으로 df 생성
4. Right Outer : 두번째 df를 기준으로 df 생성
df4 = pd.merge(df1,df2, on = 'customerID', how = 'left')>>>

df5 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on = 'customerID', how = 'outer'>>>

2. concatenate (단순 합치)
pd.concat([df1, df2]) 형태로 사용
axis 매개변수를 사용하여 행 방향(0) 또는 열 방향(1)으로 연결 방향을 지정
box1 = np.arange(1,7).reshape(2,3)
box2 = np.arange(7,13).reshape(2,3)
np.concatenate((box1,box2), axis = 1)>>>

np.concatenate((box1,box2), axis = 0>>>

ㅁ데이터 요약
1. shape : 행과 열 수 알려줌
titanic_raw = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
titanic_raw.shape>>> (891, 12) # 행, 열
2. head : 위쪽의 데이터 보여줌
titanic_raw.head()>>>

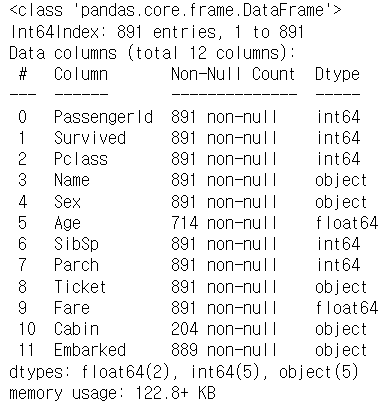
3. info : 열 정보 알려줌
titanic_raw.info()>>>
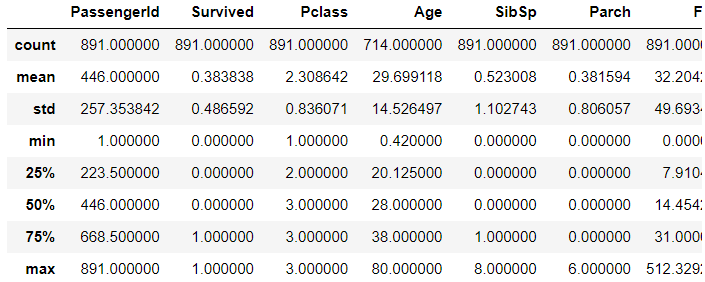
4. describe : dataframe을 통계처리하여 알려줌
>>>
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Pandas 인덱싱 하는 법 정리 (0) | 2023.08.11 |
|---|---|
| [Python] 경사도 자동 크롤링 코드 (0) | 2023.07.24 |
| [Python] VS Code 인터프리터 바꾸는 법 (아나콘다가 VS code에서 자꾸 실행될 때) (0) | 2023.07.07 |
| [Python] 모듈 datetime 및 pandas에서의 시계열 처리 (0) | 2023.07.05 |
| [Python] Beautiful Soup 과 Selenium 설치하기 (0) | 2023.04.09 |